
In 2024, just 13% of companies across the globe indicated that they were able to observe all the stages of their supply chain, including raw materials and customers. The remaining ones were unable to see all that and had to wait until they received incomplete data.
Smart traceability solution is intended to address this gap. Consider the idea of being aware of the location of your product, its performance, and who handled it, and the circumstances that it encountered, in real time. This is the future of the supply chains: all the products are the data points, and all the data points are stories.
What is Smart Traceability?, The digital heart of the modern supply chains is smart traceability. It employs contemporary technologies like IoT sensors, blockchain, AI, and digital twins to track a product from raw material to the final customer.
The conventional tracking involves barcodes and manual notes. Smart traceability captures unalterable real-time data on each product. All the activities, such as the production of the product, shipping, storage, inspection, or sale, are automatically logged. This renders the supply chain transparent and data-filled.
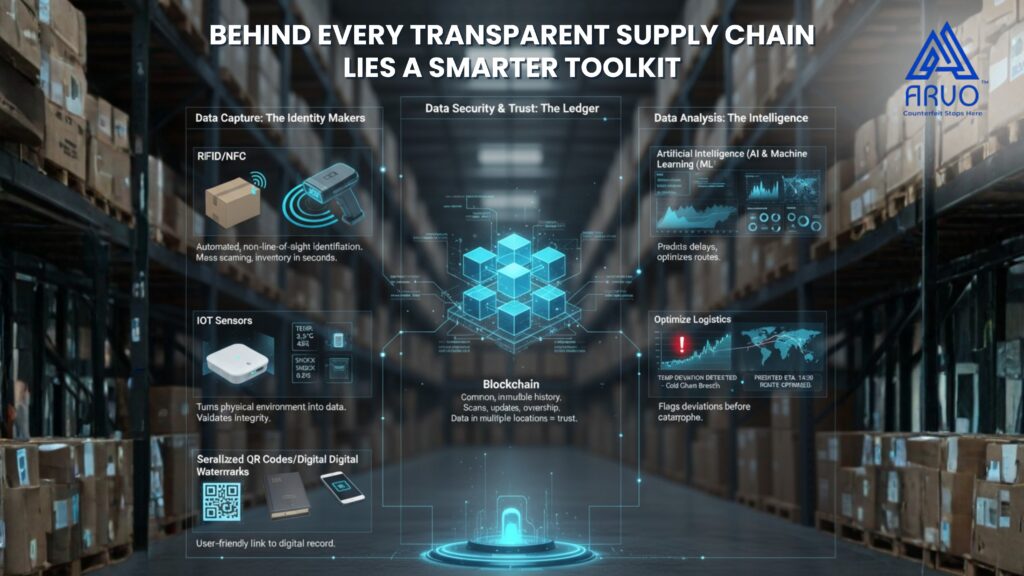
The Core Technology Toolkit
Smart traceability isn’t reliant on a single technology, but a powerful stack working in concert to create a robust data ecosystem.
Data Capture: The Identity Makers
The following technologies connect the physical product with the digital one and nourish the stream of data:
RFID/NFC: Essential for automated, non-line-of-sight identification. They enable mass scanning, inventory counts in seconds, and continuous location monitoring within a facility.
IoT Sensors (Temperature, Humidity, Shock): These are the true data transformers. They turn the product’s physical environment into measurable, traceable data points—critical for validating the integrity of perishables, pharmaceuticals, and sensitive electronics.
Serialized QR Codes/Digital Watermarks: These provide the user-friendly, accessible link to the digital data record, often used for consumer interaction.
Data Security & Trust: The Ledger
Blockchain: It is a common, immutable history of all the scans, updates and ownership transitions. Due to the fact that the data is located in a large number of locations, no single individual or corporation can alter the history of the product independently. This develops trust in all.
Data Analysis: The Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML): Collecting millions of data points is useless without intelligence. AI/ML algorithms analyze this massive flow of information to:
- Flag Anomalies: Automatically identifying deviations (e.g., a cold-chain product’s temperature spiking for 10 minutes) that signal a potential failure before it becomes a catastrophe.
- Optimize Logistics: Predicting delivery times and optimizing routes based on historical tracking data.
The Data Point Advantage: Where Products Talk
The transition to item-level data is associated with immense advantages across the chain, transforming the way business is conducted.
Improving Operations
Minor data can assist in the management of inventory and the minimization of waste. Companies have known the whereabouts of stock, and this gives:
- Accurate logistics- reduce the additional inventory since you can view products on-site and release funds.
- Counterfeit prevention- the digital identity of every product is a seal. The system will immediately alert in case one attempts to add a counterfeit item with the same ID.
Boosting Compliance & Safety
The Smart Traceability payback can be best seen in regulated industries.
- Quick, surgical recalls: A company can recall 27 units in particular stores or distribution centers instead of 10,000 pallets due to a questionable batch number, using the unique ID. This reduces liability, logistics, and brand damage.
- Automated auditing: Real-time data recording makes the cross-border, complex regulatory reporting, mandated by agencies such as the FDA or EMA, easier.
Development of Consumer Trust (The Transparency Angle)
Customers of today desire to know the origin of things. Smart traceability enables companies to tell the story of a product. The customers scan the item and view its digital passport. They will be able to view the origin of materials, certification of ethics, such as Organic or Fair Trade, and complete quality test results.

Industry Spotlight: Real-World Impact
The application of smart traceability is accelerating across high-stakes and high-value sectors, proving its strategic value.
- Food & Agriculture: The ability to trace a certain piece of meat or fruit back to the farm to the store, with temperature readings in real time, demonstrates the freshness and is safe. It also allows the company to maintain the shelf life longer and recall only the affected ones, avoiding large supply-chain issues.
- Pharmaceuticals: Global requirements, such as smart traceability, are necessary to monitor the path of vials of serotonin-treated medicines across the globe with the help of a secure registry. It destroys counterfeit drugs and provides cold-chain compliance to sensitive vaccines and specialty drugs.
- Luxury Goods & Fashion: By adding a special NFC tag or digital watermark to designer handbags or watches, companies can add the item to a safe ledger. This offers genuineness in the resale markets that are of high value and combats the illegal market of trade.
Challenges and Future Outlook
To overcome initial challenges, Scaling Smart Traceability must overcome the following primary ones:
Interoperability: Establishing common standards of data to ensure the smooth exchange of data between systems and competitors.
Initial investment: RFID readers, sensors, and the construction of new software may be expensive to purchase.
But the path is clear. The fundamental technology behind an Autonomous Supply Chain is Smart Traceability, a technology that enables data to make decisions in real-time, and those decisions are self-correcting. It also opens the real Circular Economy, allowing companies to trace products to disassemble, refurbish, and recover materials, generating a new and valuable piece of data: the recyclability passport of the product.
Conclusion: The Takeaway
Smart traceability is not merely an IT upgrade; it is a fundamental shift in business model, turning overhead (tracking) into asset creation (data). It empowers every tangible asset, from a microchip to a mango, to become an intelligent, verifiable data source that drives efficiency, secures compliance, and builds unshakeable customer trust.
For ventures and enterprises looking to secure a competitive edge in the next decade, investing in and adopting smart traceability is non-negotiable. It is the mechanism by which physical goods will communicate their value, their history, and their future potential.
FAQ
How does AI assist with smart traceability?
AI examines the vast quantity of data that sensors produce. It identifies issues, anticipates risks, and assists in transporting goods more effectively. As an example, it will be able to predict delays, prevent spoilage, and detect fake products immediately.
What is the benefit of blockchain in improving traceability?
Blockchain stores the records of products in a distributed network, hence nobody can alter them. All the changes are recorded in a permanent transparent ledger, and this creates confidence among the manufacturers, suppliers, and customers.
What is the difference between smart traceability and traditional tracking systems?
The conventional tracking involves barcodes and manual data entry that may be slow and provide incomplete information. Smart traceability records data automatically and provides tamper-proof technology to provide real-time, continuous supply-chain tracking.
What does smart traceability hold in the future?
Autonomous supply chains will be the result of smart traceability that will automatically rectify itself. Information will flow freely across systems, and decisions will be made without human involvement. It will also aid in the development of credible, open-minded circular economies.